Graphene: Ultra-Light, High-Strength Material for Enhanced Product Performance
Reading Time: 2 minutes
In recent years, graphene has gained immense interest due to its unique physical properties and the exciting opportunities it presents for applications in multiple industries. Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms that are tightly bound together in a hexagonal honeycomb pattern. This material is light, flexible and incredibly strong. In fact, it’s the lightest and strongest material ever measured. In addition to its incredible strength, graphene is able to conduct heat and electricity better than any other known material. It’s also the thinnest substance ever made.
Many compounders have been adding graphene nanoplatelet technology to their formulas to extend the lifetime and strength of their finished products. Graphene nanoplatelets are unique nanoparticles comprised of multiple layers of graphene sheets. Each layer has a particle diameter of fewer than 2 microns and a typical particle thickness of a few nanometers, depending on the surface area.
Graphene nanoplatelets offer numerous benefits including energy savings, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, barrier properties, lubricity, and processing efficiency. Adding graphene nanoplatelets to formulas helps manufacturers meet specific performance requirements and deliver better products to end-users.
Excellent conductivity in electronics
Because graphene nanoplatelets are so flexible and have excellent electrical properties, they are often used in electrical applications such as consumer electronic devices. Using graphene nanotechnology, electronics manufacturers can make smartphones and tablets that are much more durable and flexible enough to bend without breaking.
Graphene’s use in electronics extends beyond consumer devices. This remarkable material shows immense potential for a range of biomedical applications, including drug delivery, cancer therapies, and biosensors.
Improved performance in elastomeric oil and gas parts
Graphene applications in the oil and gas industry are numerous. Green graphene nanoplatelets, or nanoplatelets produced through green manufacturing processes, have demonstrated exceptional performance in various petrochemical applications.
Green graphene nanotechnology increases tensile strength, elongation, and resistance to high temperatures, abrasion, and corrosion. In many cases, less energy and less material are required to develop parts, greatly reducing the environmental footprint of manufacturing processes.
Green graphene nanoplatelets are ideal for a variety of elastomeric oil and gas parts:
- Casing and isolation packers
- Stators and rotors
- Valves & Seals
- Conductive EMI, RFI shielding gaskets
- Pump liners
- Blowout preventers
- Hose and pipe
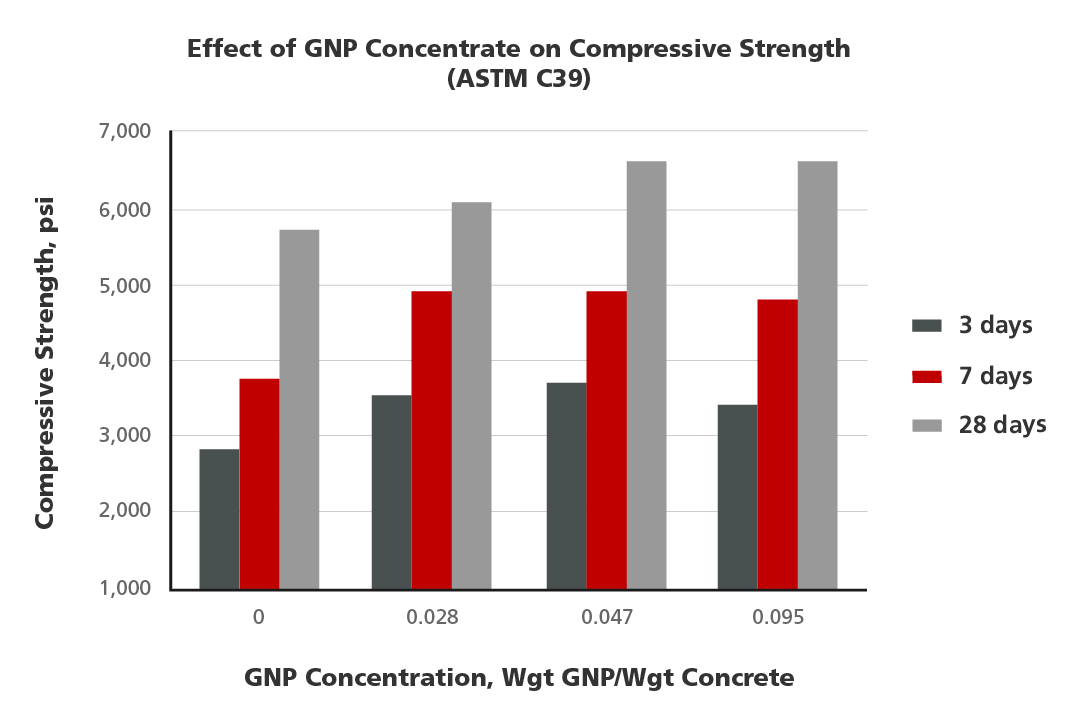
Increased compressive strength in cement applications
Graphene-reinforced cement is two times stronger than cement without graphene. It’s more durable and more resistant to corrosion, acid attacks, water, and gas permeability. Incorporating graphene into cement-based materials also provides synergistic results in combination with other reinforcements (i.e., microspheres, pozzolans and fibers).
H.M. Royal partners with largest graphene producer
The demand for graphene is growing rapidly. Manufacturers need to find a vendor they can trust and who can ensure fast, reliable delivery of the materials they need to be successful.
Recently, H.M. Royal and CenoStar partnered with XG Sciences, the largest producer of graphene in the United States. Partnering with XG Sciences allows H.M. Royal to deliver XG Sciences’ graphene nanoplatelets — as well as CenoStar cenospheres and hollow glass microspheres — to support the production needs of customers in multiple industries.
We provide a full line of graphene nanoplatelets in varying sizes and surface areas. And eco-friendly options are available to help you realize significant energy savings and minimize your carbon footprint.
To learn more about graphene nanoplatelets or for help selecting the right solution for your application, contact H.M. Royal today.
 (800) 257-9452
(800) 257-9452


